Kikuchi Disease Pathology Outlines
Kikuchi disease pathology outlines. O Sm1 slight submucosal invasion 200 -300µm02 03mm o Sm2 intermediate between sm1 and sm3 o Sm3 invasion into deep aspect of submucosa. In the wake of this many examples of this lesion. A 26-year-old man was hospitalized with a 1-month history of fever.
Head and neck pathology. 50 linhas Kikuchi disease is a benign non-cancerous condition of the lymph nodes. Kikuchi disease also known as apoptotic lymphadenitis or histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis is a benign self-limiting condition of unknown etiology.
KikuchiFujimoto disease KFD also known as Kikuchi disease is a rare lymphohistiocytic disor-der first described in 197212 KFD generally affects women of Asian descent between the ages of 20 and 35 years and has a malefemale ratio of 12. Howev-er new cases of KFD have also been described in. Kikuchis disease KD is an idiopathic self-limited necrotizing lymphadenitis that can clinically and histologically mimic high-grade lymphoma including Hodgkins disease or can be mistaken for the lymphadenitis of systemic lupus erythematosus SLE.
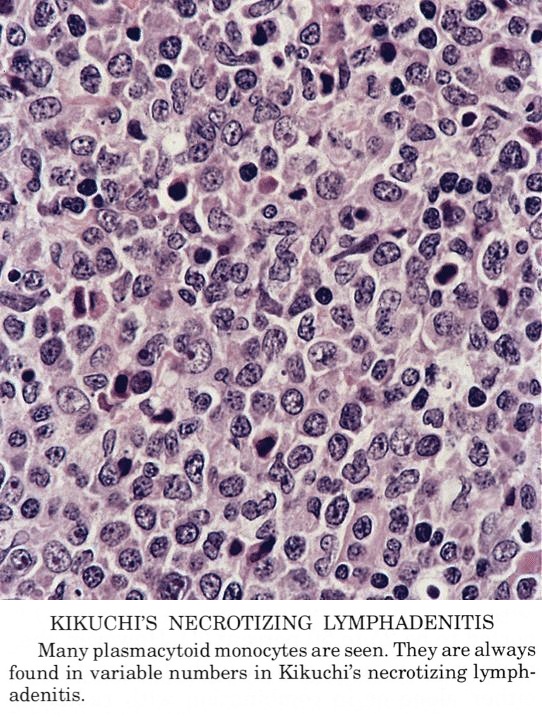
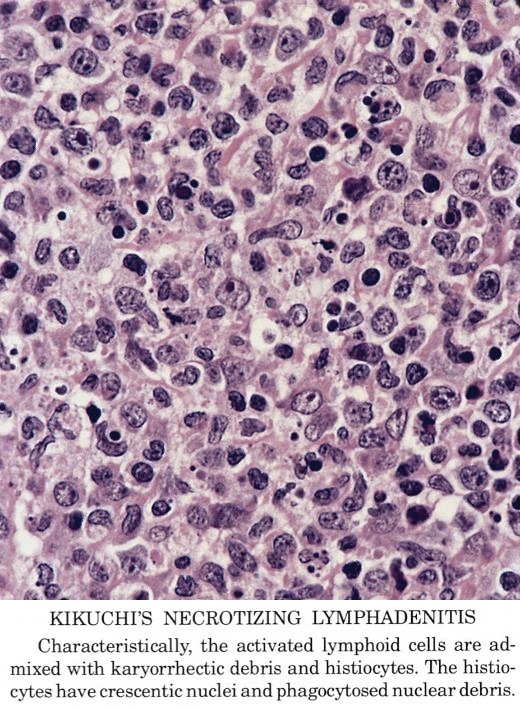
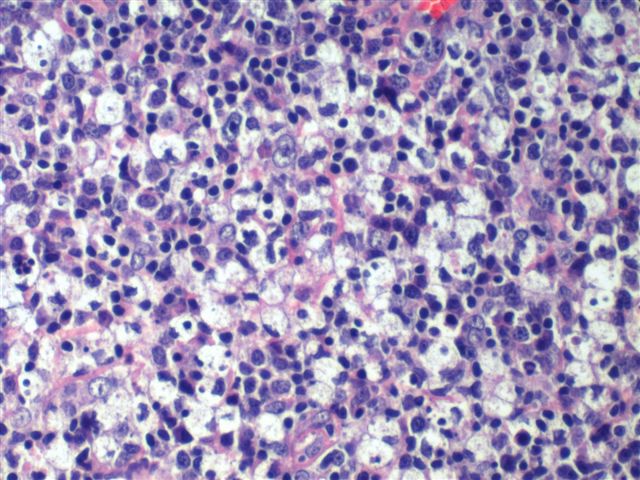
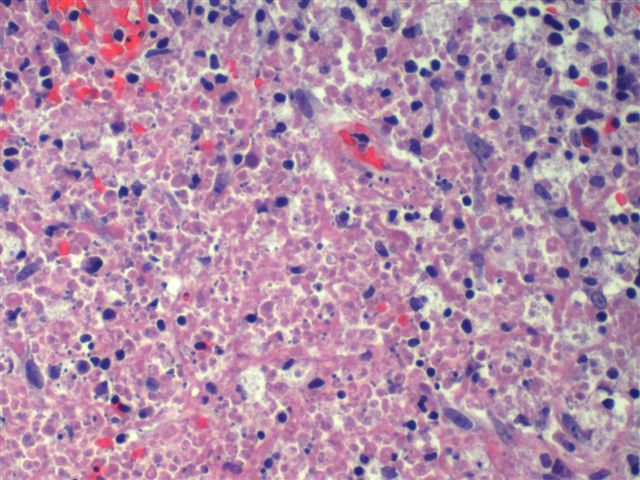
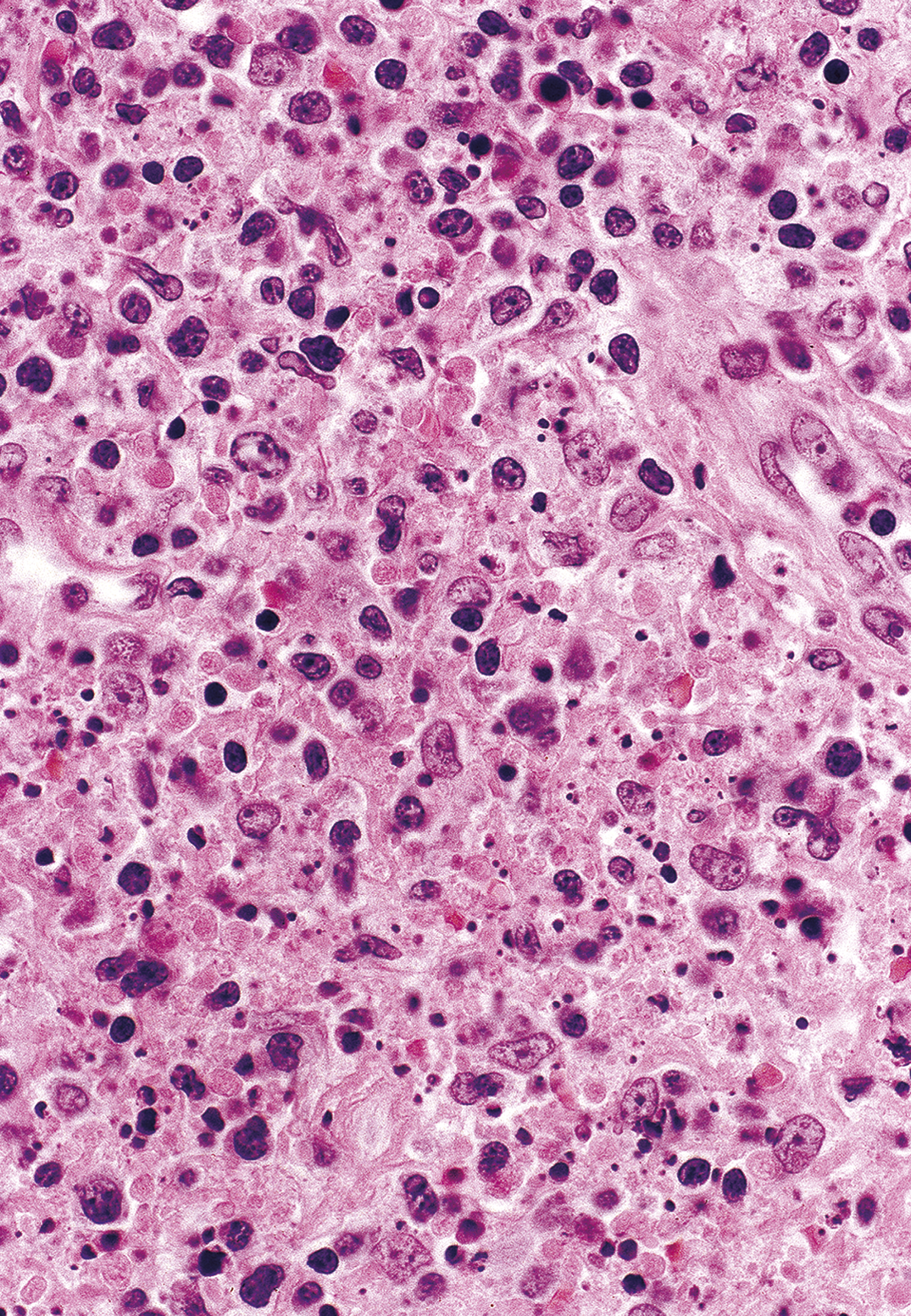
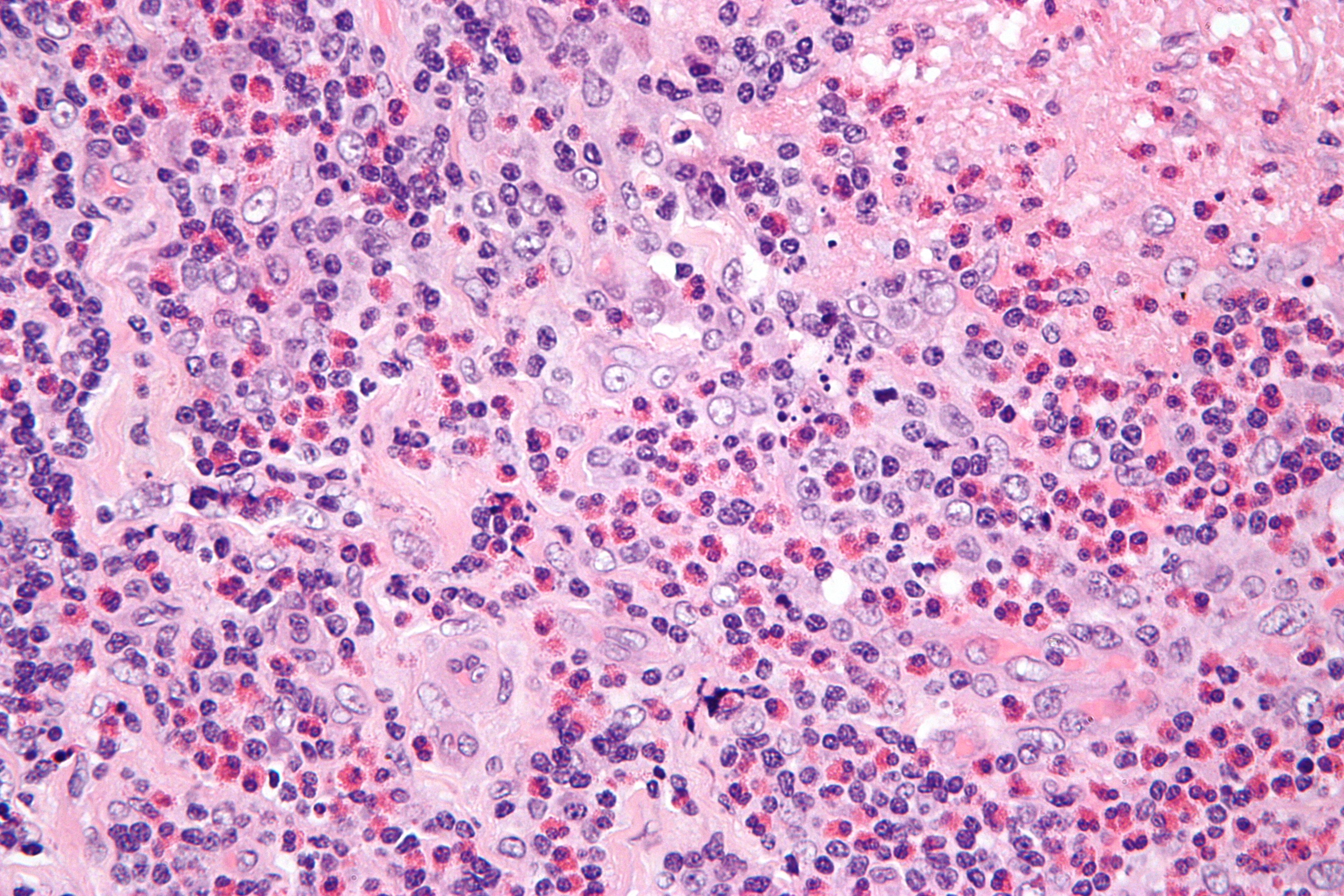
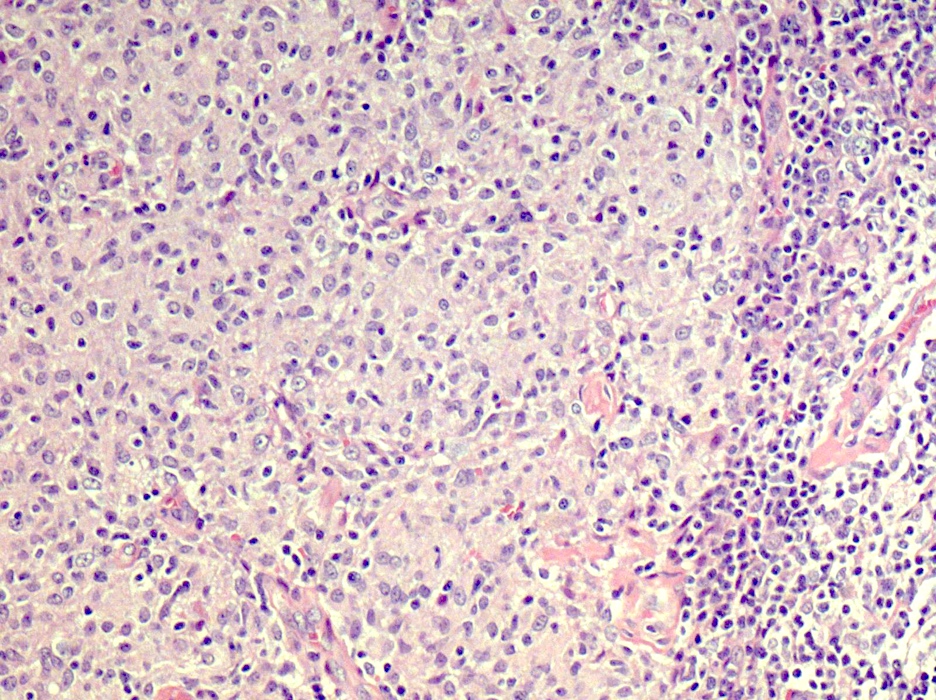
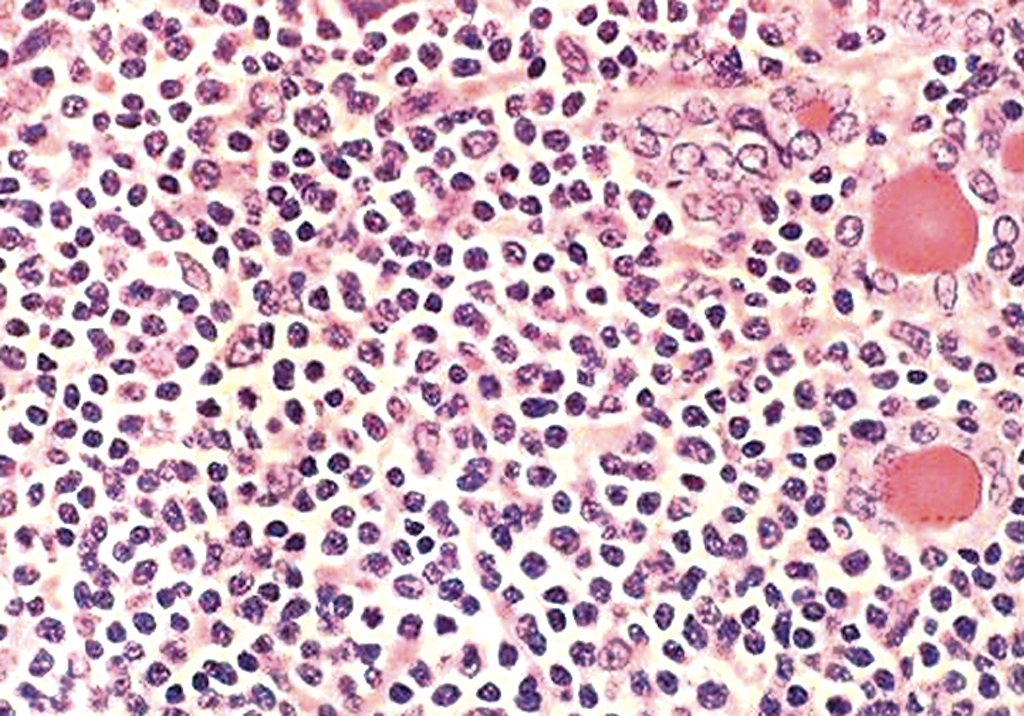
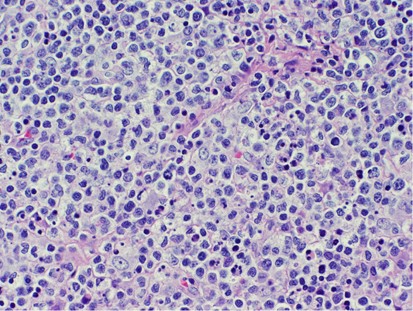
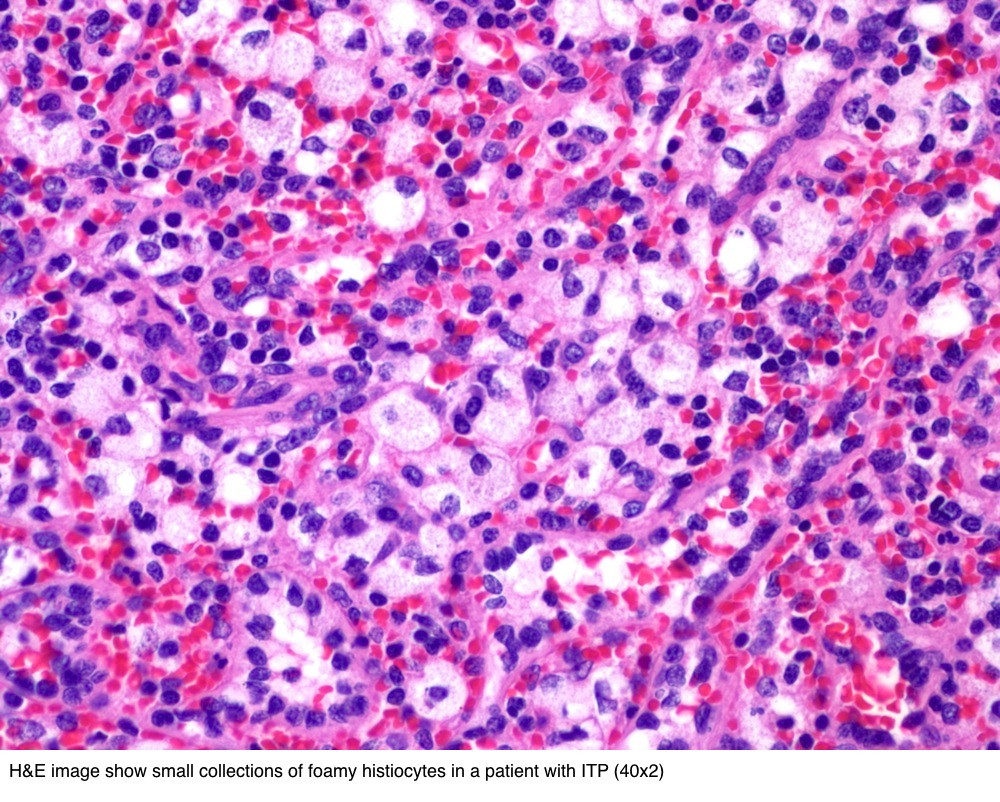
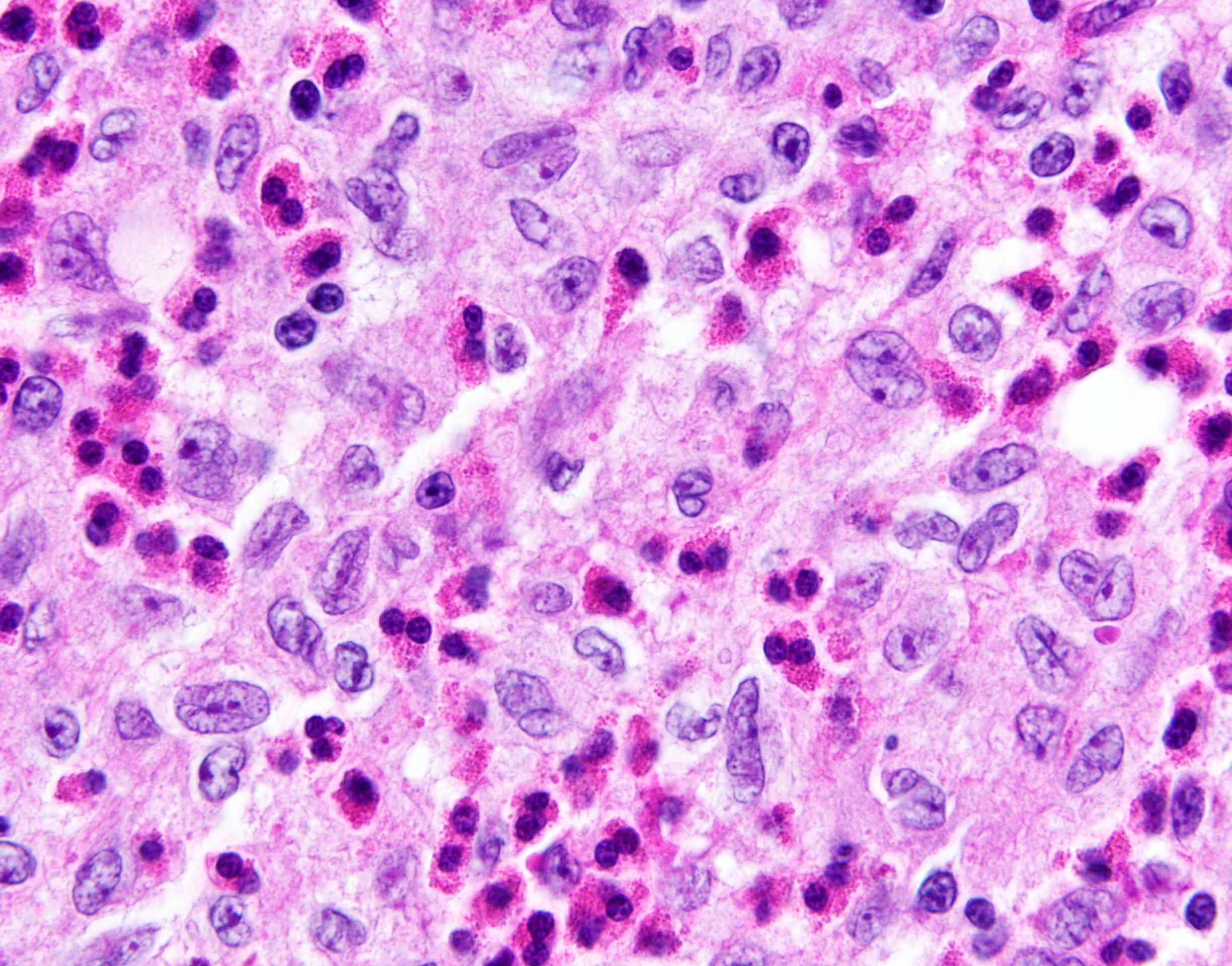
Findings in four cases ofthe disease were evaluated. This disorder also called histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis and Kikuchis disease was initially described in Japan and other Asian countries but now is found worldwide It primarily affects young women who present with cervical lymphadenopathy tender or painless fever and often leukopenia The etiology is unknown although the prominent necrosis is due to apoptosis mediated by cytotoxic T. Karryorhexis fibrin deposits plasmacytoid monocytes 2 - 3x size of small lymphocytes variable cytoplasm round nuclei with open chromatin small nucleoli CD4 that may resemble lymphoma phagocytic and foamy histiocytes T cells CD8 cytotoxic phenotype.
In 1972 Kikuchi and Fujimotoet a2 described an unusual lymphadenitis which they called lym-phadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia withnucleardebrisandphagocytosis andcervical subacute necrotising lymphadenitis respectively. 23 24 25 26 It most commonly affects young Asian. Are applicable to sessile or semi-sessile polyps and record the depth of invasion into submucosa sm in a 3 grade system.
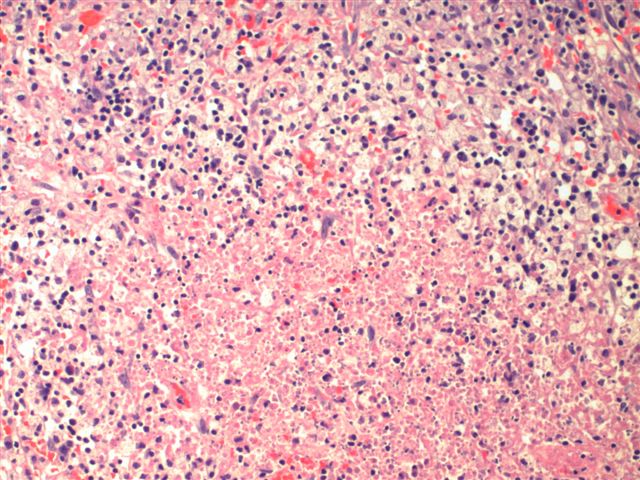
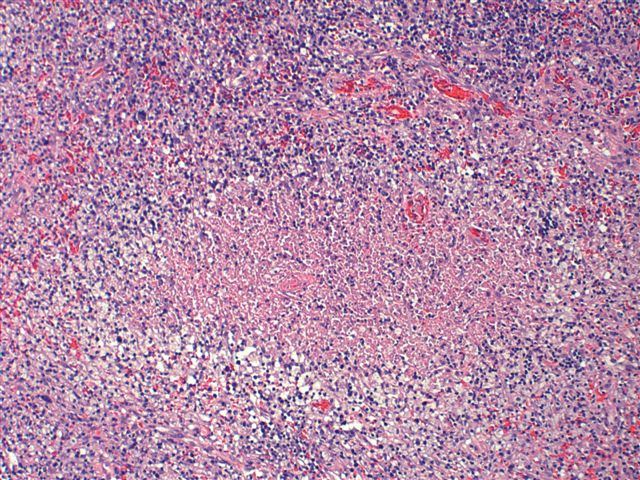
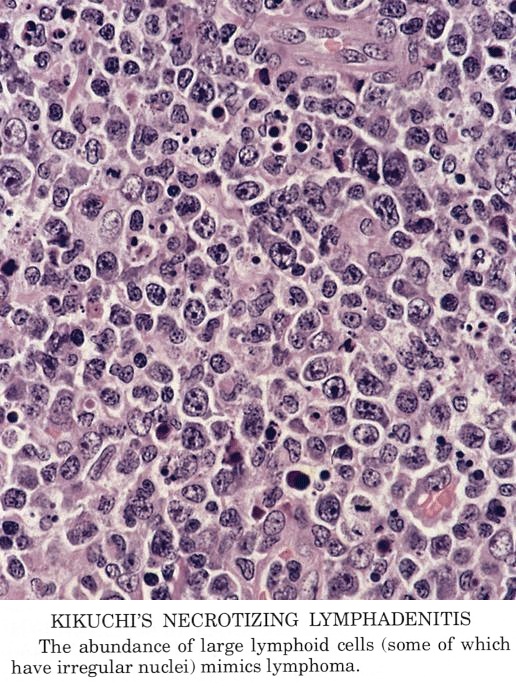
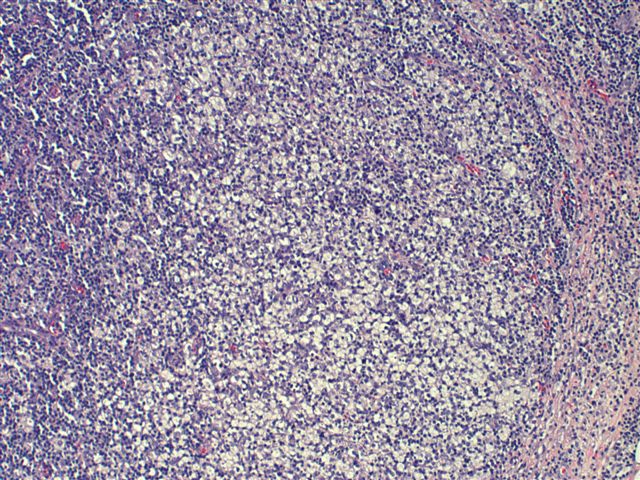
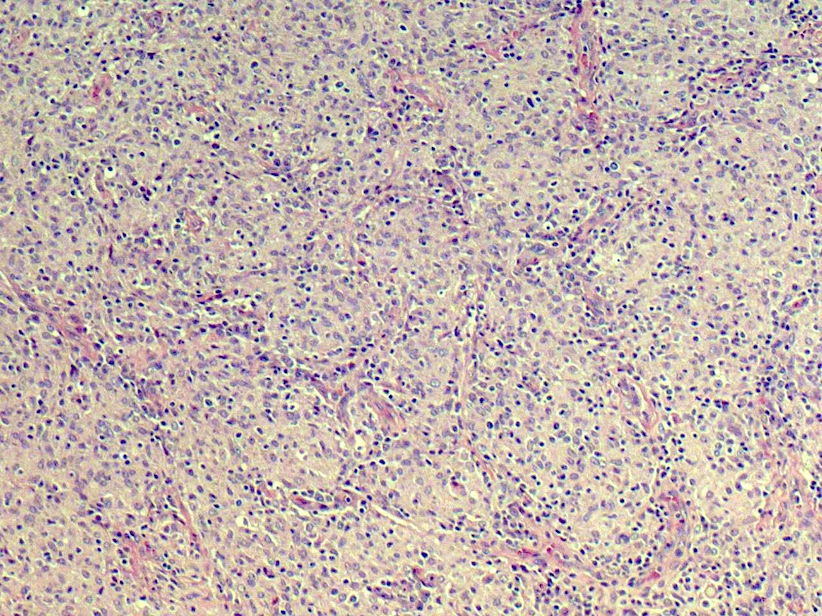
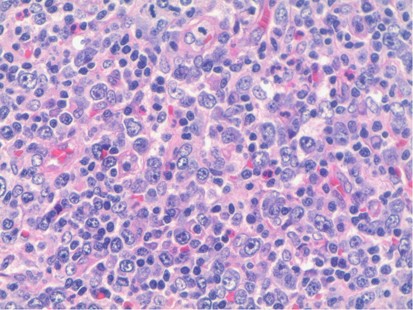
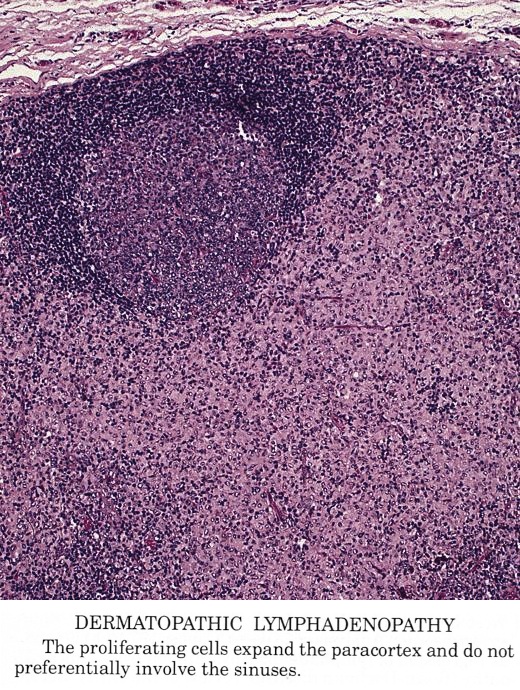
Characteristic triad of reactive germinal centers perifollicular clusters of epithelioid histiocytes and islands of monocytoid cells. This disease which has a broad morphologic spectrum can readily be mistaken for malignant lym-phoma. Clinically and histologically this disease can be mistaken for lymphoma or SLE 2 6 16 17 Hence differentiating this from common lymphadenopathic conditions is extremely vital.
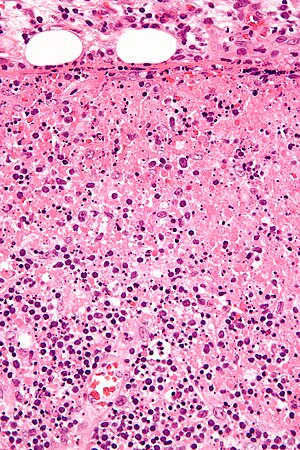
Cervical lymph node biopsy showed necrosis in the paracortical area with abundant nuclear debris and proliferation of histiocytes. No loss of T cell antigens.
Aberrant loss of T cell antigens common.
Karryorhexis fibrin deposits plasmacytoid monocytes 2 - 3x size of small lymphocytes variable cytoplasm round nuclei with open chromatin small nucleoli CD4 that may resemble lymphoma phagocytic and foamy histiocytes T cells CD8 cytotoxic phenotype. 50 linhas Kikuchi disease is a benign non-cancerous condition of the lymph nodes. This disease which has a broad morphologic spectrum can readily be mistaken for malignant lym-phoma. Findings in four cases ofthe disease were evaluated. Characteristic triad of reactive germinal centers perifollicular clusters of epithelioid histiocytes and islands of monocytoid cells. In the wake of this many examples of this lesion. This disorder also called histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis and Kikuchis disease was initially described in Japan and other Asian countries but now is found worldwide It primarily affects young women who present with cervical lymphadenopathy tender or painless fever and often leukopenia The etiology is unknown although the prominent necrosis is due to apoptosis mediated by cytotoxic T. Involvement of extranodal sites is unusual bu. Kikuchis disease KD is an idiopathic self-limited necrotizing lymphadenitis that can clinically and histologically mimic high-grade lymphoma including Hodgkins disease or can be mistaken for the lymphadenitis of systemic lupus erythematosus SLE.
In the wake of this many examples of this lesion. 50 linhas Kikuchi disease is a benign non-cancerous condition of the lymph nodes. Karryorhexis fibrin deposits plasmacytoid monocytes 2 - 3x size of small lymphocytes variable cytoplasm round nuclei with open chromatin small nucleoli CD4 that may resemble lymphoma phagocytic and foamy histiocytes T cells CD8 cytotoxic phenotype. This disorder also called histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis and Kikuchis disease was initially described in Japan and other Asian countries but now is found worldwide It primarily affects young women who present with cervical lymphadenopathy tender or painless fever and often leukopenia The etiology is unknown although the prominent necrosis is due to apoptosis mediated by cytotoxic T. Characteristic triad of reactive germinal centers perifollicular clusters of epithelioid histiocytes and islands of monocytoid cells. KikuchiFujimoto disease KFD also known as Kikuchi disease is a rare lymphohistiocytic disor-der first described in 197212 KFD generally affects women of Asian descent between the ages of 20 and 35 years and has a malefemale ratio of 12. Kikuchi disease also known as apoptotic lymphadenitis or histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis is a benign self-limiting condition of unknown etiology.


















Post a Comment for "Kikuchi Disease Pathology Outlines"