Neonatal Polycystic Kidney Disease
Neonatal polycystic kidney disease. It is caused by mutations of the PKHD1 gene polycystic kidney and hepatic disease-1 also known as ciliary IPT domain containing fibrocystinpolyductin on chromosome 6p12. ARPKD is the neonatal form of PKD and is associated with enlarged kidneys and biliary dysgenesis. MIM263200 is one of the most frequent pediatric renal cystic diseases with an incidence of 120000 1.
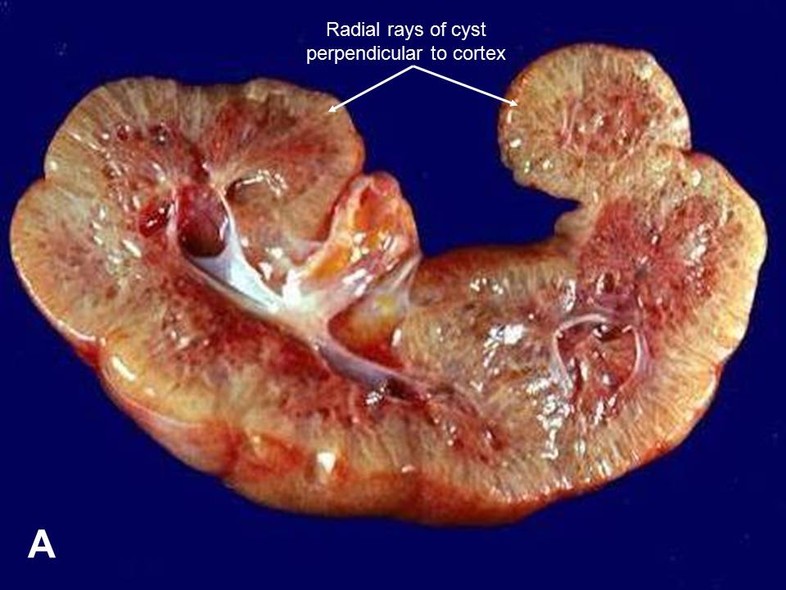
These cysts can reduce kidney function leading to kidney failure. The severe perinatal form of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease maps to chromosome 6p211p12. Longitudinal retrospective cohort study.
Thus Wedekin et al reported an incidence of 1 in 10000 live births in the studied geographic area. 420 children mean age 83 -. Polycystic kidney disease in children.
The disease phenotype is highly variable ranging from neonatal death to later presentation with minimal kidney disease. When the kidneys fail to function the only life-extending options are dialysis and kidney. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is a genetic disorder that causes the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys.
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD. The incidence of CKD at this age is very difficult to establish due to the low number of studies available in the literature. A case report Despite the poor prognosis of PKD reported in the literature our case had an outstandingly favorable evolution during the first 2 years of life most-likely due to the early diagnosis and treatment but also proper monitoring.
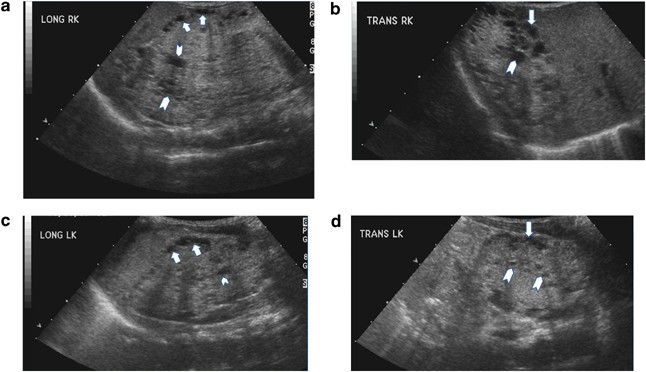
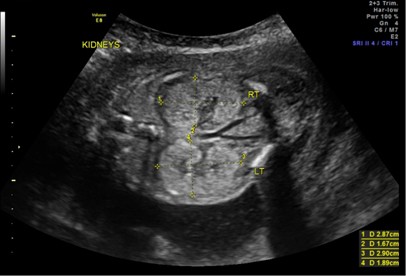
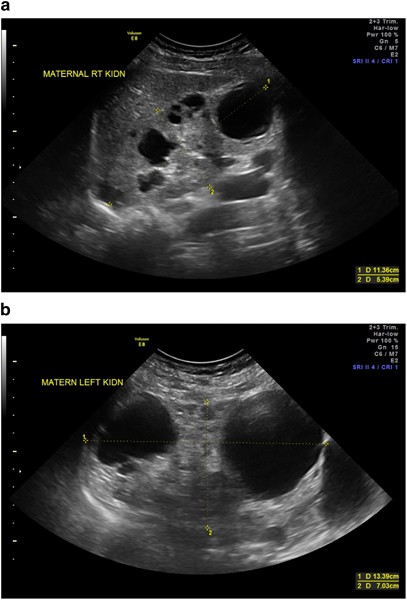
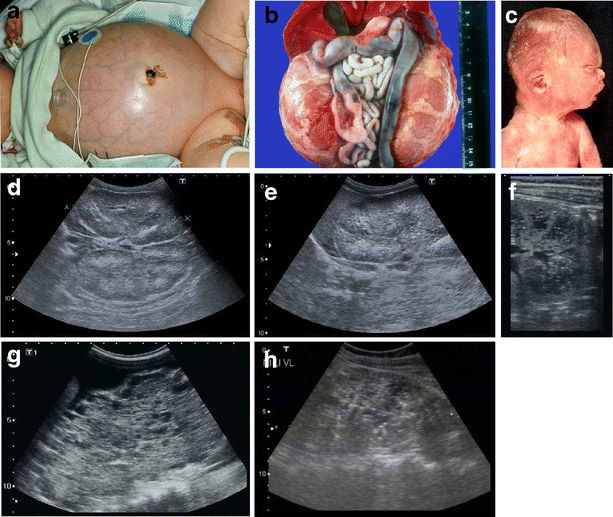
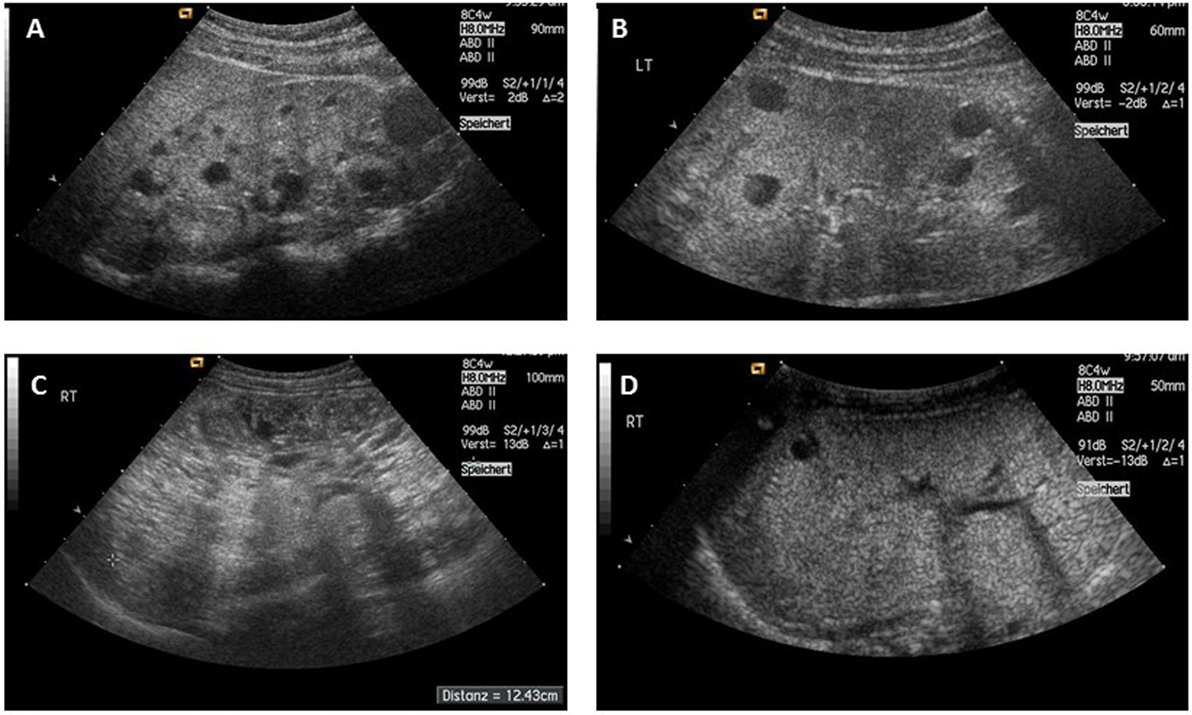
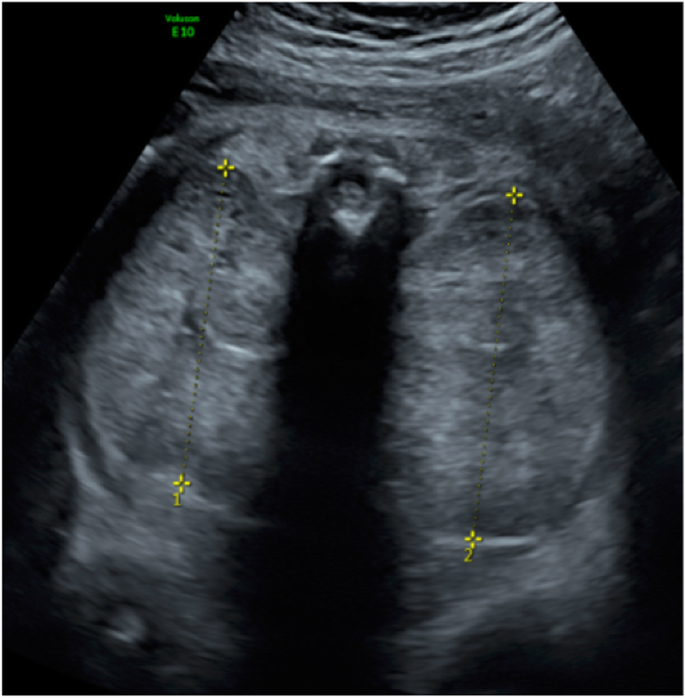
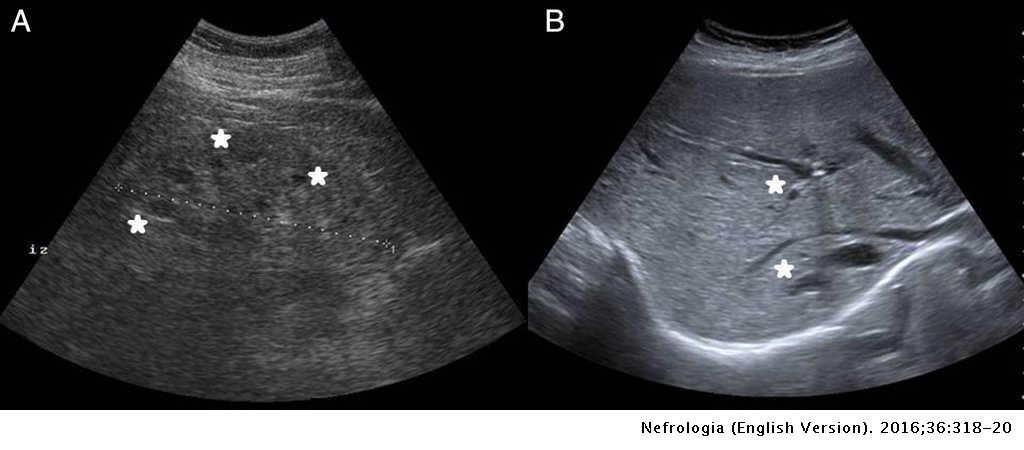
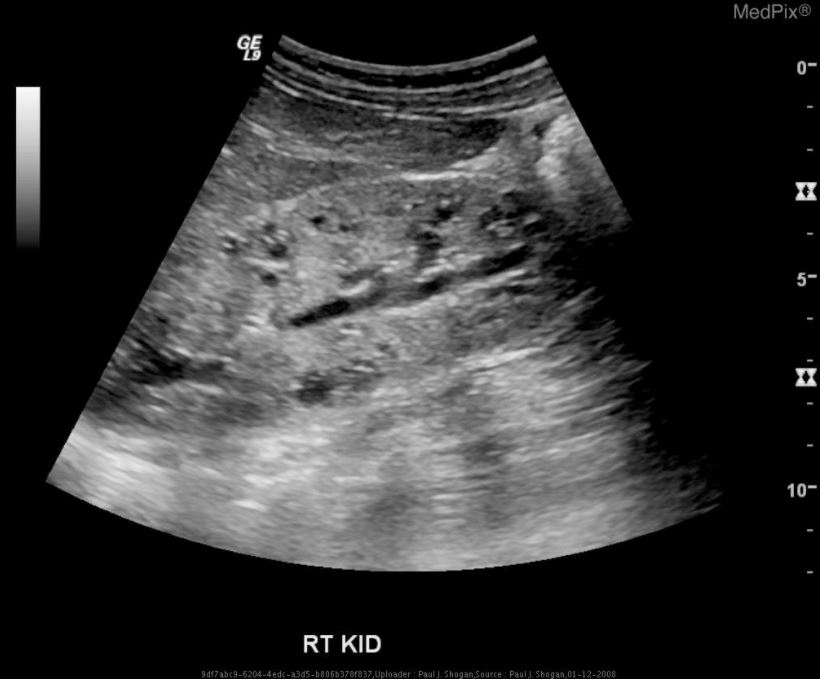
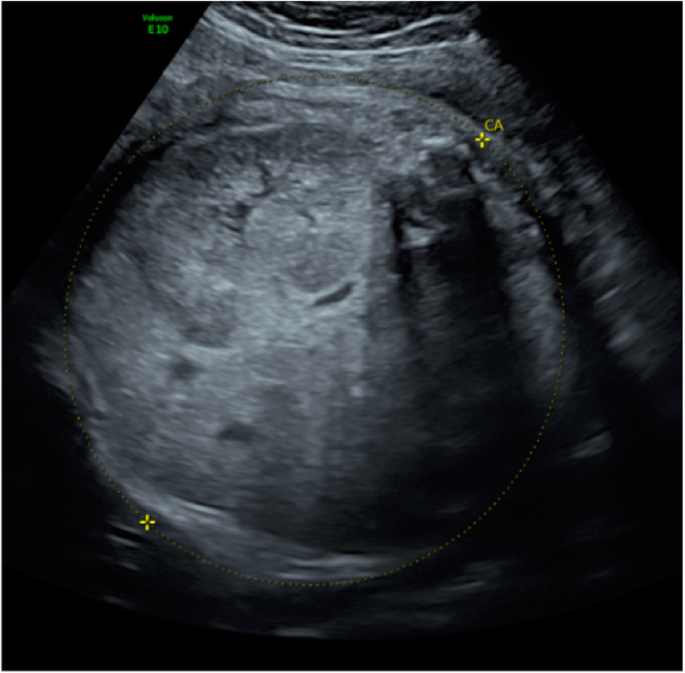
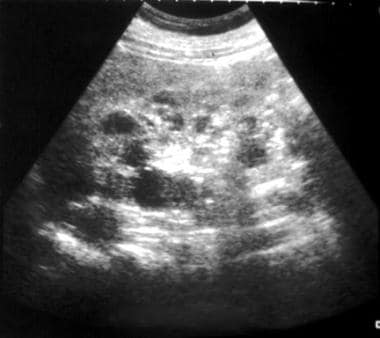
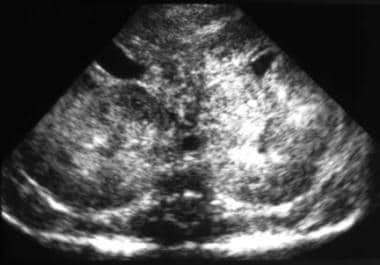
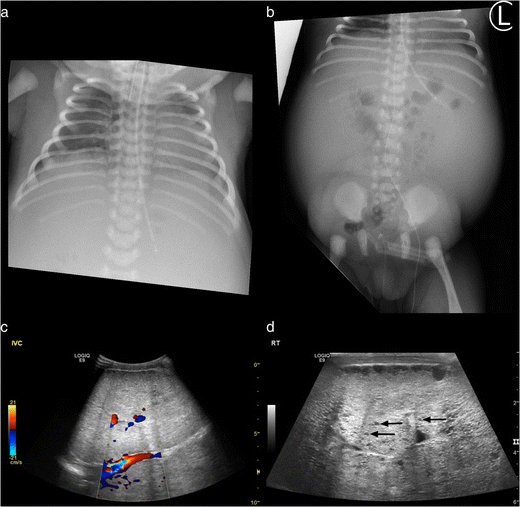
ARPKD is often identified during the prenatal and neonatal periods due to strikingly large poorly functioning echogenic kidneys. To date there are no criteria for diagnosing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD in at-risk children 15 years or younger. Neonatal polycystic kidney disease a potential life-threatening condition at this age.
The majority of individuals with ARPKD present in the neonatal period with enlarged echogenic kidneys. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a systemic disease with progressive development of fluid-filled cysts in both kidneys as a major characteristic.
When the kidneys fail to function the only life-extending options are dialysis and kidney.
The disease phenotype is highly variable ranging from neonatal death to later presentation with minimal kidney disease. This article provides an up-to-date comprehensive review and summary on neonatal polycystic kidney disease PKD with emphasis on the differential diagnosis clinical manifestations diagnostic techniques and potential therapeutic approaches for the major causes of neonatal PKD namely hereditary disease including autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant PKD and. Polycystic kidney disease in children. The formation of numerous cysts together with interstitial fibrosis usually causes chronic renal failure beyond mid life. A case report Despite the poor prognosis of PKD reported in the literature our case had an outstandingly favorable evolution during the first 2 years of life most-likely due to the early diagnosis and treatment but also proper monitoring. It can lead to kidney failure. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a systemic disease with progressive development of fluid-filled cysts in both kidneys as a major characteristic. When the kidneys fail to function the only life-extending options are dialysis and kidney. MIM263200 is one of the most frequent pediatric renal cystic diseases with an incidence of 120000 1.
This entity which is now referred to as autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease and congenital hepatic fibrosis ARPKD-CHF 2 is characterized by. It can lead to kidney failure. Neonatal diagnosis of PKD was considered when some of the neonates presented palpable flank masses that caused fetal dystocia. Polycystic kidney disease PKD is a rare genetic disorder. Prenatal ultrasonography results were correlated with positive family history of polycystic kidney disease PKD fetal enlarged kidneys and oligohydramnios. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD. MIM263200 is one of the most frequent pediatric renal cystic diseases with an incidence of 120000 1.


























Post a Comment for "Neonatal Polycystic Kidney Disease"