Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease Disability
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease disability. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease. If you suffer from mixed connective tissue disease that is so severe you are unable to work you may be approved for Social Security disability benefits. He described UCTD as having overlapping symptoms of lupus rheumatoid arthritis and myositis without it being any of those more well-known diseases.
In many cases the distinction between symptoms of connective tissue disease and complications of connective tissue disease is unclear. The SSA breaks musculoskeletal disorders into the following categories. Although a third of UCTDs can progress to a definite ARD.
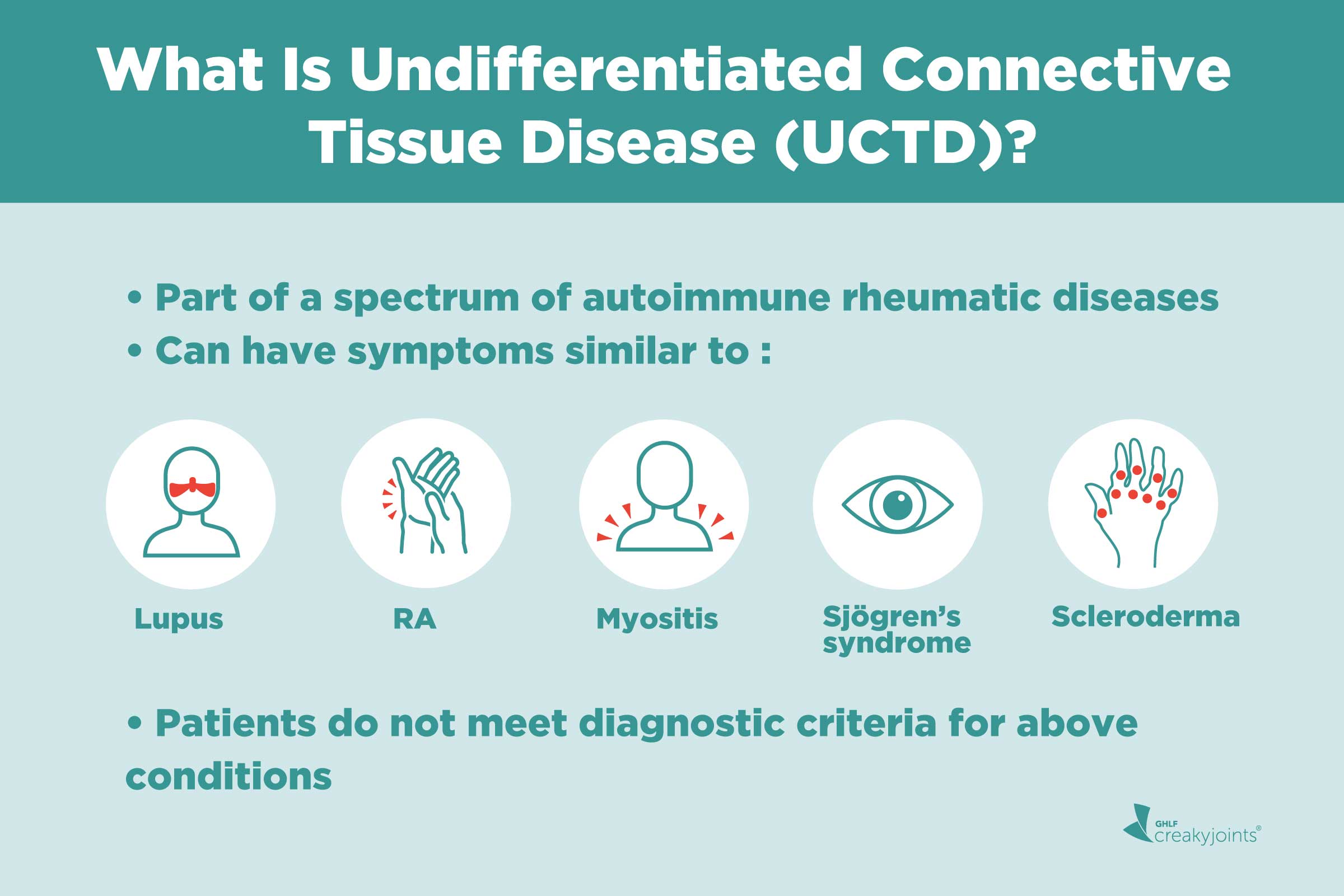
The term undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD refers to unclassifiable systemic autoimmune diseases which share clinical and serological manifestations with definite connective tissue diseases CTDs but not fulfilling any of the existing classification criteria. Complications of connective tissue disease are secondary conditions symptoms or other disorders that are caused by connective tissue disease. It is a disorder that has not yet developed to a point where doctors can easily identify the disease.
Mixed connective tissue disease has signs and symptoms of a combination of disorders primarily lupus scleroderma and polymyositis. My doctor told me it was an autoimmune disease called undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD. This means at times you may almost wish you were dealing with a different illness one people have heard of and doctors seem to understand better.
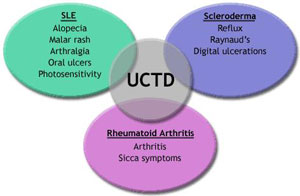
The guidelines laid out in the Blue Book for deciding disability claims for musculoskeletal disorders relate primarily to how the disability affects your ability to move perform tasks and concentrate on a job. No colored ribbon associated with UCTD. The term undifferentiated connective tissue diseases is used to define conditions characterized by the presence of signs and symptoms suggestive of a systemic autoimmune disease that do not satisfy the classificative criteria for defined connective tissue diseases CTD such as systemic lupus erythematosus SLE Sjögrens syndrome SS rheumatoid arthritis RA and others.
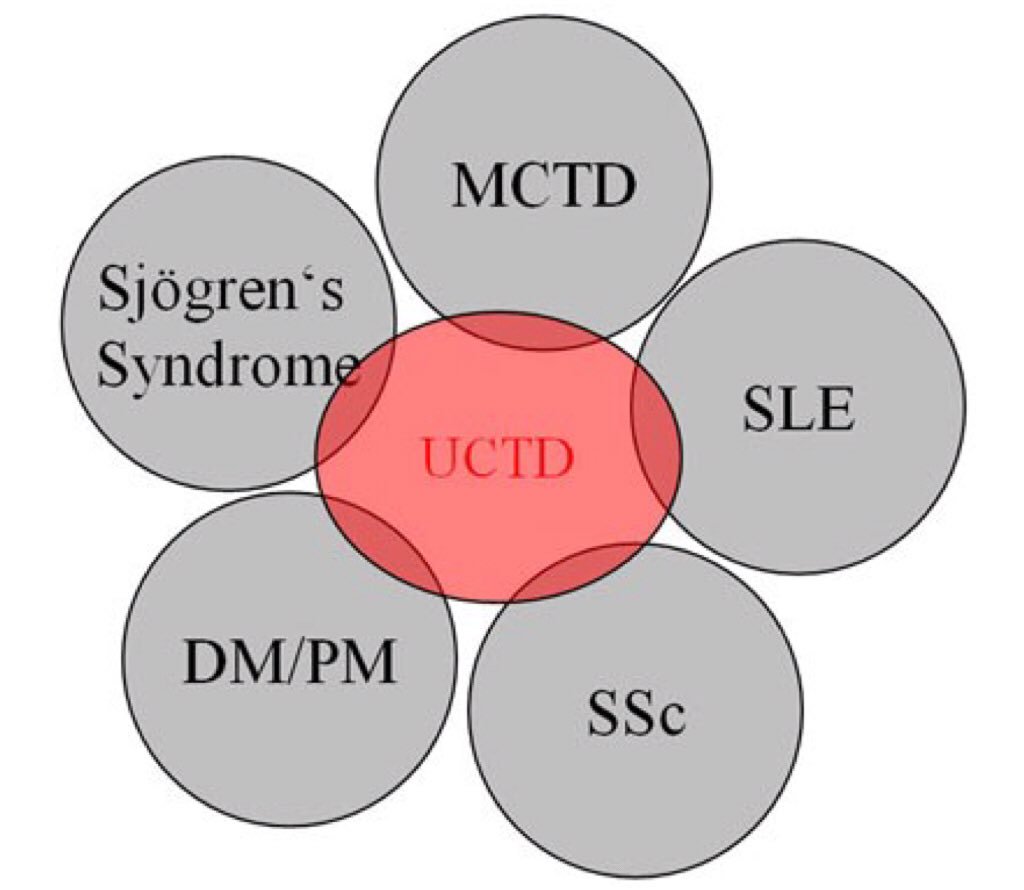
Connective tissue disease CTD is classified as undifferentiated CTD when signs and symptoms are consistent with a CTD but do not fulfill the diagnostic or classification criteria for one of the previously defined CTDs for example rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. For this reason mixed connective tissue disease is sometimes referred to as an overlap disease. Undifferentiated connective tissue diseases UCTDs are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by symptoms and signs suggestive of systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease ARD but which do not fulfill all the established criteria for definite diagnosis of a condition.
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease describes people who have certain laboratory markers and clinical characteristics that suggest a systemic autoimmune disorder or connective tissue disease. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD is an autoimmune disease that can affect several systems in the body.
For this reason mixed connective tissue disease is sometimes referred to as an overlap disease.
In many cases the distinction between symptoms of connective tissue disease and complications of connective tissue disease is unclear. In many cases the distinction between symptoms of connective tissue disease and complications of connective tissue disease is unclear. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease is diagnosed when clinical features and serologic blood test findings such as rheumatoid factor or antinuclear antibody consistent with an autoimmune disorder are present but do not satisfy the criteria for a specific disease. The guidelines laid out in the Blue Book for deciding disability claims for musculoskeletal disorders relate primarily to how the disability affects your ability to move perform tasks and concentrate on a job. The term undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD refers to unclassifiable systemic autoimmune diseases which share clinical and serological manifestations with definite connective tissue diseases CTDs but not fulfilling any of the existing classification criteria. It is a disorder that has not yet developed to a point where doctors can easily identify the disease. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease. My doctor told me it was an autoimmune disease called undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD. This means at times you may almost wish you were dealing with a different illness one people have heard of and doctors seem to understand better.
Mixed connective tissue disease MCTD is diagnosed when clinical features and serologic findings of two or more autoimmune. My doctor told me it was an autoimmune disease called undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Those with mixed connective tissue disease or undifferentiated connective tissue disease may qualify for Social Security disability benefits if your condition meets the SSAs Blue Book listing. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease describes people who have certain laboratory markers and clinical characteristics that suggest a systemic autoimmune disorder or connective tissue disease. The SSA breaks musculoskeletal disorders into the following categories. The term undifferentiated connective tissue diseases is used to define conditions characterized by the presence of signs and symptoms suggestive of a systemic autoimmune disease that do not satisfy the classificative criteria for defined connective tissue diseases CTD such as systemic lupus erythematosus SLE Sjögrens syndrome SS rheumatoid arthritis RA and others.









































Post a Comment for "Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease Disability"